Please note, many of the bold words in this overview display hidden content when you roll your mouse over them.
Lesson
The Skeletal System, The Muscular System
Introduction
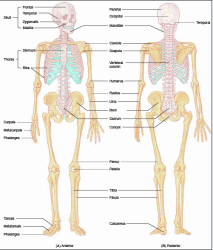
The Skeletal System
The muscular system and skeletal system are often referred to as the "musculoskeletal system." The muscles, joints, and bones work together, providing a framework for support and movement. Bones are hard and dense, made of compact minerals, and help to protect delicate internal organs, such as the brain, the heart, and the spinal cord. The growth of long bones from the ends (epiphyseal plates) allows us to attain our adult height.
Besides providing a framework for the body, the bones protect the internal organs from exposure and injury, and store calcium, a mineral that is necessary for bone density and hardness. Some related combining forms are:
- oss/e, oss/i
- oste/o, ost/o
Learn more about The Structure of Bone. (The interactive has audio.)
Click here for the Transcript.
Hematopoiesis is the term used to describe the formation of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in red bone marrow. Yellow bone marrow serves as a fat storage area for fat cells. A related combining form is:
- myel/o
Joints are places where two or more bones come together, termed "articulations." Freely movable joints, such as those along the vertebral column, allow us a wide range of motion, including bending and turning at various angles. Other joints, such as the suture joints in the skull, are tightly knit and immovable, providing added protection for the underlying brain tissue.
Cartilage is connective tissue that cushions the ends of bones, acts as a shock absorber, and allows ease of movement at joints. A related combining form is:
- chondr/o
Ligaments connect one bone to another. A related combining form is:
- ligament/o
The Muscular System
Muscles permit external movement since they are attached to bones. Internal movement of muscles allows certain organs to perform their jobs, such as the constant beating of the heart, the contractions of the diaphragm, and the rhythmic contractions of the uterus during childbirth.
The muscular system's primary function is to make body movement possible. A related combining form is:
- my/o, myos/o
Learn more about Types of Muscle Tissue. (The interactive has audio.)
Click here for the Transcript.
The fascia primarily functions to cover, support, and separate muscles. A related combining form is:
- fasci/o
There are four muscle classifications:
Learn more about Muscle Contraction and Relaxation (The interactive has audio.)
Click here for the Transcript.
Glossary of Mouseover Terms
| Glossary of Mouseover Terms Used in Lecture | |
|---|---|
| Term | Mouseover Popup |
Antagonists | Oppose or reverse a particular movement |
Fixators | Synergists that immobilize a bone or muscle's origin |
Forms | Combining forms are created by adding a vowel (usually the letter 'o') to the end of a word root |
Myel/o | Combining form meaning marrow, but also means spinal cord |
Oste/o | Combining form meaning bone |
Prime movers | Provide the major force for producing a specific movement |
Synergists | Add force to a movement, reduce undesirable or unnecessary movement |
Review
Click on the link above to test your knowledge of this week's material.
Note: These activities will open in a new pop-up window, so you may need to disable any pop-up blockers.
This review is not graded. You may take the review as many times as you like.
 Flash Cards
Flash Cards